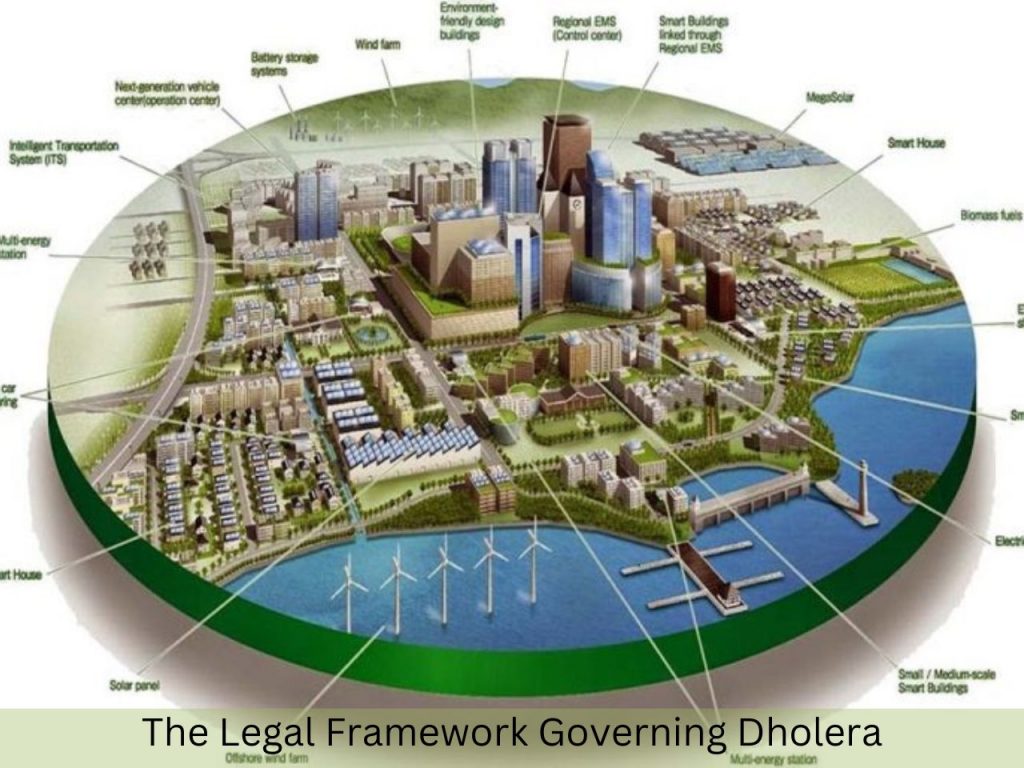
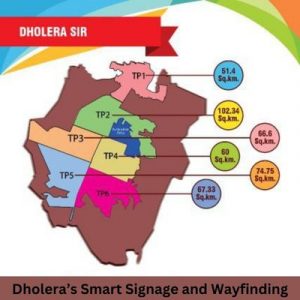
Dholera is an ancient port city located in Gujarat. India is currently being developed into a smart city under the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) project. This ambitious project aims to transform Dholera into a global manufacturing and trading hub. The legal framework governing Dholera is multifaceted. This includes various laws, regulations, and guidelines that aim to ensure that development is sustainable, inclusive, and legally sound.
Historical Context and Vision
Dholera’s history as a trading port dates back over a millennium, which has influenced its cultural and economic fabric. The vision for Dholera Smart City is to revive this historical significance by creating a modern urban center. This can compete on a global scale. This vision is supported by the Special Investment Region Act of 2009. Which provides a legal foundation for the establishment and management of the region.

Special Investment Region Act
The Special Investment Region (SIR) Act was enacted. This is to create a framework for setting up, operating, and regulating Special Investment Regions like Dholera. The Act outlines the powers and functions of the Regional Development Authority. This is responsible for planning and developing the SIR. It also details the process of land acquisition, compensation, and rehabilitation of affected persons. This ensures that the development is just and fair.
Environmental Regulations
Given the scale of the project, environmental sustainability is a critical concern. The Environment Protection Act of 1986, along with various notifications such as the Environmental Impact Assessment Notification of 2006, governs the environmental regulatory framework. These laws mandate rigorous environmental impact assessments and ensure that all development activities comply with environmental standards.
Land Acquisition and Rehabilitation
Land acquisition for Dholera SIR has been a contentious issue, and the legal framework seeks to address this through the Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation, and Resettlement Act of 2013. This Act ensures that land acquisition is done in a manner that provides fair compensation, rehabilitation, and resettlement to the affected landowners and communities.
Infrastructure Development
The development of infrastructure in Dholera is governed by the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Model, which encourages collaboration between the government and private entities. The Model Concession Agreement provides a legal contract that outlines the roles, responsibilities, and risk-sharing mechanisms between the public and private partners.
Governance and Administration
The governance structure of Dholera is designed to be efficient and responsive. The Gujarat Town Planning and Urban Development Act of 1976, along with the DMIC Project Implementation Trust, provides the administrative and financial framework for the planning and development of urban infrastructure.
Investment and Trade Laws
To attract investment, Dholera is governed by pro-business laws such as the Special Economic Zones Act of 2005, which offers tax incentives and eases regulatory burdens for businesses operating within the zone. Additionally, the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999 regulates foreign investment and ensures that international trade complies with Indian laws.
Intellectual Property and Innovation
As a hub for manufacturing and innovation, protecting intellectual property is crucial. The Indian Patent Act of 1970, along with the Copyright Act of 1957, provides a legal framework for protecting inventions, designs, and creative works, fostering an environment conducive to innovation.
Labor Laws and Workforce Development
The development of Dholera also focuses on creating employment opportunities. The Industrial Disputes Act of 1947, the Minimum Wages Act of 1948, and other labour laws ensure that workers’ rights are protected and that there is a skilled workforce to support the industries.
Conclusion
The legal framework governing Dholera is comprehensive, addressing various aspects of development, from land acquisition to environmental sustainability, and from governance to trade. As Dholera progresses towards becoming a smart city, it is this robust legal structure that will ensure its development is sustainable, equitable, and aligned with the broader goals of economic growth and innovation.